Picture lock for George was originally scheduled for 4th of December and to be completed 12 days later ready for hand-in on December 16th. We have received the final cut of the picture on the 12th of January, leaving us 8 days to complete as much of the audio as possible in time for the film groups hand-in on the 20th, and with another 7 days in hand to polish up for our own hand-in on the 27th. Whilst this is, on the face of it, a reasonably similar timeframe for completion, it is complicated by the disruption to our workflow caused by the extension and the Christmas break, the fact that our advance facilities bookings assumed the earlier completion date which means it became more difficult to access the facility we have committed to technically, and the incoming pressure of organising our impending Semester B studies. This provision of multiple versions of the picture for different deadlines at different times was then further complicated by the unexpected request for a copy of the film with most of the key audio devices included and as much of the music completed as possible on the 16th, to enable the media production group to critique the film for their paperwork.
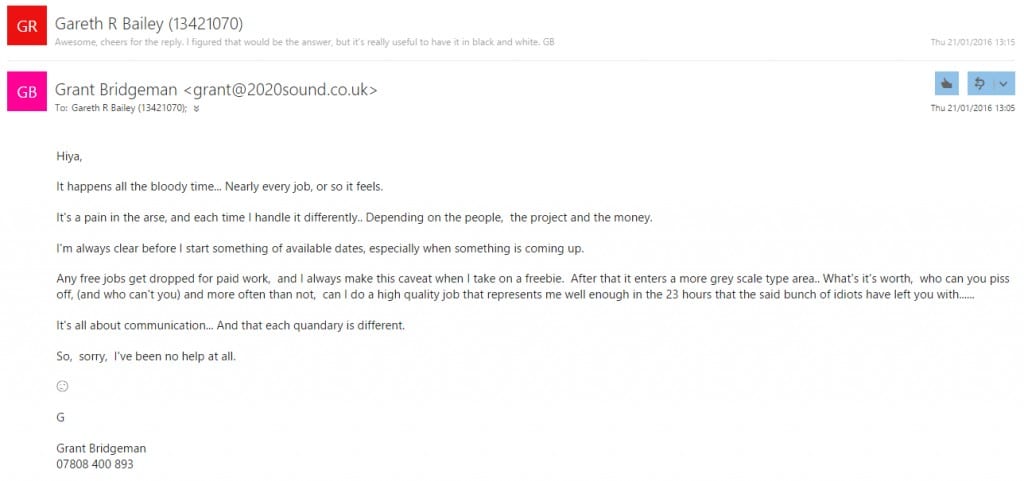
Taking the audio for a 16 minute film from 50% complete to around 85% complete in 4 days with limited access to facilities is obviously nigh-on impossible to achieve to any reasonable standard, especially given that the length of titles and credits (requiring hefty alterations to music compositions) were not made available until the day of delivery of picture lock. Due to the client-employee relationship of this particular project there was no disincentive for the director to begin requesting mixdowns earlier and earlier as soon as the edits were complete, all of which further interrupted our workflow and took the priorities on the project out of our hands. We managed to provide what was requested largely on time, and I was prompted to consider this situation as it would pan out in the real-world and the possibility of some kind of contractual stipulation on clients for recompense or renegotiation in the case of overrun’s of this type, as the complications here have impacted our planning for Semester B work and a similarly protracted project would likely cause problems for a schedule of work. I ran the question of whether such a thing is ever formalised past Grant Bridgeman by email for the benefit of his experience…He pointed out that this situation comes to pass on ‘almost every job’, and that he deals with it on a case by case basis judged on existing relationships with the client. For me, that’s about as succinct a description of the way creative freelancing works in practice as any I’ve seen.
For Grant, the malleability of deadlines as in the case of George is inevitable and it’s all about how you deal with it, and the relationship with the client. Practically, realistic projections of the amount of work that can be accomplished in the timeframe should be furnished to the client, which brings the whole point here back to communication. I was confident in our ability to deliver the bulk of the work even for the close deadline when communicating with our client, but should perhaps have been more cautious in my appraisal of specifically what we were able to deliver by certain dates.
As per my role within the production, I’ve tried very hard throughout to keep communication with the client about their audio requirements to a maximum, and I see this as a useful and successful aspect of the project from my own perspective, given the fact that the film has effectively had two directors (from our perspective that is, the film was co-directed by all four people in the group, but I requested a single point of contact with the team from the outset to minimise potential for confusion). The second director altered a number of the first director’s artistic decisions as far as the sound and music of the film is concerned, which meant essentially rerunning the process of the earlier spotting sessions with the second director to see if requirements were to change. I could have foreseen this likelihood earlier and discussed her requirements immediately when she agreed to be point of contact for us upon the departure of the first director as it’s critical to remind the creative lead for the picture they are also the creative lead for the audio team, to my mind.
More specifically on communication, I realised it is vital when (even basic) audio tracklaying work has begun in parallel with picture editing (an imperfect situation at best, but unavoidable given the circumstances of this production), to hammer home the critical nature of good edit logging with an editor who is working on the piece – The third cut of the film we received had no accompanying information on alterations to the footage we’d begun work on, which roughly doubled the time it took us to resync our audio. We did mention to the editor previously that we needed this information but didn’t receive it, so this must be communicated with more force in the future. Again, this situation is apparently fairly standard in film work and it tallies with the view of John Purcell,
‘It’s much more common to run into postlock changes than to work on a movie whose structure is set in stone,’ (Purcell, 2008, 239)
The use of temp music tracks is also worthy of note as the receipt of them by our director represents a classic example of something we were warned about in Lol Hammond’s guest lecture. The 2nd director had had little time to think about the music for the piece, was clearly surprised at the impact even basic composition can have on the picture, and rapidly became accustomed to the temp tracks we provided despite our admonishments not to do so as these were for suggestion only. This was fortuitous in a sense as she asked for the songs to be kept simple (like the skeletal temp tracks), which saved us a certain amount of production time, but unfortunate in that we had to back away from our plans for more complex original compositions for the piece. This is something to be very wary of in the future, as it could just as easily have worked in the opposite direction and caused us further complications.
– 1000 Words
Key Points –
Reflection on post production interaction with director, and delivery requests – Process Management, Individual reflection on learning and team role.
- To manage the delivery of the soundtrack at various stages of the production along with relevant paperwork, to the director and producer.
Application of skills and conduct in production
Reflection on post production interaction with editor – Process Management, Individual reflection on learning and team role.
- To successfully manage the audio team’s interaction with film’s director, editor and producer on a practical and creative level, and ensure the audio team’s work is delivered on time and to a good standard.
Application of skills and conduct in production
Reflection on use of temporary music cues – Process Management, Individual reflection on learning.
- To contribute extensively to the practicalities of creating and recording music for, and of recording location sound for the piece.